Difference Between AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning: A Clear and Simple Guide
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) are terms often thrown around in tech conversations, but they can feel like a maze of jargon to the uninitiated. If you’ve ever wondered what sets them apart or how they work together, you’re not alone. These concepts are interconnected yet distinct, and understanding their differences can unlock a clearer perspective on the tech shaping our world. In this article, we’ll break down AI, ML, and DL in a natural, human-friendly way, ensuring you walk away with a solid grasp of each. Let’s dive in!
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence is the big umbrella term. It’s the science of creating machines or systems that can mimic human intelligence to perform tasks. Think of AI as the grand vision of making computers think and act like humans—whether that’s recognizing images, understanding speech, or even making decisions.
AI isn’t a new idea; it’s been around since the 1950s when pioneers like Alan Turing asked, “Can machines think?” Today, AI powers everything from your smartphone’s voice assistant to recommendation algorithms on streaming platforms. At its core, AI is about enabling machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, like problem-solving, reasoning, or learning from experience.
For a deeper dive into how AI is transforming industries, check out AI Mastery Plan for practical insights on leveraging AI in your projects.
Types of AI
AI comes in different flavors, each with its own scope:
- Narrow AI: This is the AI we interact with daily. It’s designed for specific tasks, like Siri answering your questions or Netflix suggesting shows. Narrow AI excels at one thing but can’t generalize to other tasks.
- General AI: This is the sci-fi dream—AI that can perform any intellectual task a human can. We’re not there yet, but researchers are working toward it.
- Superintelligent AI: A hypothetical future where AI surpasses human intelligence. It’s more speculative than practical for now.
AI is the foundation, and Machine Learning is one of its most powerful tools. Let’s explore ML next.
What is Machine Learning (ML)?
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on teaching machines to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. Instead of hard-coding rules for every scenario, ML algorithms analyze patterns in data and improve over time as they process more information.
Imagine teaching a child to recognize cats. You could show them thousands of cat pictures, and they’d eventually figure out what makes a cat a cat—whiskers, pointy ears, and all. ML works similarly. You feed it data (like images or numbers), and it learns to make predictions or decisions based on patterns it finds.
For example, ML powers spam filters by learning to spot suspicious emails based on examples. It’s also behind fraud detection systems, which analyze transaction patterns to flag anomalies. Curious about real-world ML applications? SupportClaim.info offers case studies on how ML is used in industries like finance and healthcare.
How Machine Learning Works
ML algorithms typically fall into three categories:
- Supervised Learning: The algorithm is trained on labeled data (e.g., “this is a cat, this is not”). It learns to predict outcomes, like whether an email is spam or not.
- Unsupervised Learning: The algorithm works with unlabeled data, finding hidden patterns. Think of clustering customers into groups based on shopping habits.
- Reinforcement Learning: The algorithm learns by trial and error, receiving rewards for good decisions. It’s how AI learns to play games like chess or Go.
ML is powerful, but it often relies on structured data and human guidance. That’s where Deep Learning takes things further.
What is Deep Learning (DL)?
Deep Learning is a specialized subset of Machine Learning, inspired by the human brain’s neural networks. It uses artificial neural networks—layers of interconnected nodes—to process vast amounts of data and identify complex patterns. DL is what makes modern AI so impressive, especially in tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous driving.
Think of DL as ML on steroids. While traditional ML might struggle with raw, unstructured data like images or audio, DL thrives on it. For instance, DL powers facial recognition by analyzing pixel patterns in photos or enables chatbots to understand nuanced human speech.
To explore how DL is revolutionizing tech, AI Mastery Plan has excellent resources on building DL models for your projects.
How Deep Learning Works
DL’s magic lies in its neural networks, which mimic how neurons in the brain process information. These networks have:
- Input Layer: Where raw data (like an image’s pixels) enters.
- Hidden Layers: Where the real processing happens, detecting features like edges, shapes, or even emotions in text.
- Output Layer: Where the final prediction or classification is made (e.g., “this is a dog”).
DL requires massive datasets and significant computational power, often using GPUs or specialized chips. It’s why DL breakthroughs have surged with advancements in hardware and cloud computing.
For a deeper look at DL’s technical side, SupportClaim.info breaks down how neural networks are trained for cutting-edge applications.
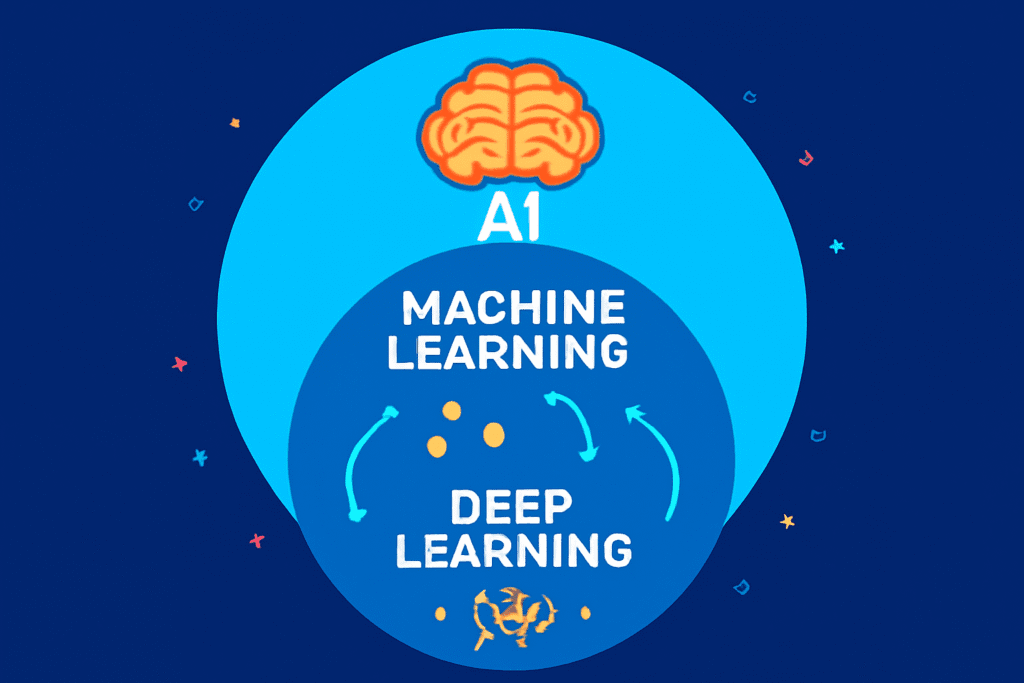
Key Differences Between AI, ML, and DL
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s clarify the differences:
- Scope:
- AI: The broadest concept, encompassing any technique that enables machines to mimic human intelligence.
- ML: A subset of AI, focusing on algorithms that learn from data.
- DL: A subset of ML, using neural networks to handle complex, unstructured data.
- Complexity:
- AI: Includes simple rule-based systems (like early chess programs) and advanced ML/DL models.
- ML: Requires structured data and feature engineering (humans selecting relevant data features).
- DL: Handles raw data and automatically extracts features, but needs more data and computing power.
- Applications:
- AI: Powers everything from chatbots to robotics.
- ML: Used in recommendation systems, fraud detection, and predictive analytics.
- DL: Excels in image recognition, speech processing, and autonomous systems.
- Data Dependency:
- AI: Can work with minimal data in rule-based systems.
- ML: Needs moderate, structured data.
- DL: Demands massive, often unstructured data.
- Human Involvement:
- AI: Varies—some systems need heavy human input, others less.
- ML: Requires humans to select features and prepare data.
- DL: Automates feature extraction, reducing human intervention.
Why Does This Matter?
Understanding these distinctions helps you appreciate the tech behind everyday tools. When you ask a voice assistant a question, AI orchestrates the response, ML interprets your speech patterns, and DL might analyze the audio’s nuances. Each layer builds on the others, creating smarter, more capable systems.
For businesses, knowing the difference guides technology choices. A small company might use ML for customer segmentation, while a tech giant might invest in DL for self-driving cars. For individuals, it’s about staying informed in a world increasingly shaped by intelligent machines.
Getting Started with AI, ML, and DL
If you’re eager to explore these fields, start small:
- Learn AI Basics: Platforms like AI Mastery Plan offer beginner-friendly guides to AI concepts.
- Experiment with ML: Try tools like scikit-learn for simple ML projects or dive into case studies on SupportClaim.info.
- Explore DL: Use frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch to build neural networks, starting with tutorials on image classification.
The Future of AI, ML, and DL
The lines between AI, ML, and DL will continue to blur as technology evolves. AI is becoming more accessible, ML is getting smarter, and DL is pushing boundaries in fields like healthcare and entertainment. By understanding their differences, you’re better equipped to navigate this exciting landscape.
Whether you’re a curious beginner or a seasoned techie, the journey into AI, ML, and DL is full of possibilities. So, what’s your next step? Dive into a project, explore a course, or simply marvel at how these technologies are reshaping our world.
